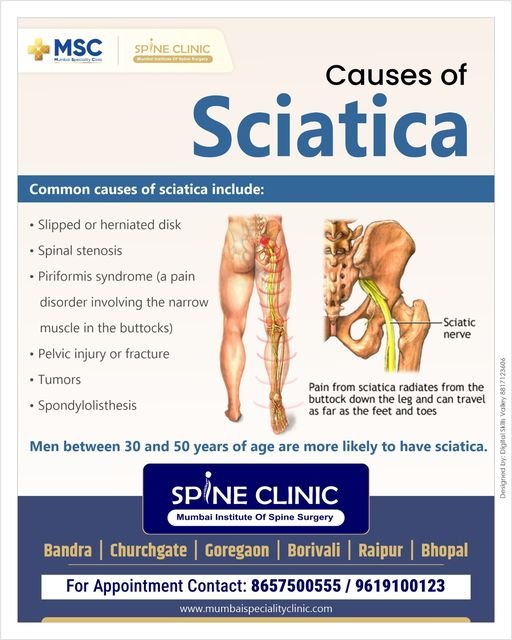
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. This pain can vary in intensity and is often accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected leg. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for sciatica can help manage this condition effectively.
What is Sciatica?
Sciatica is not a diagnosis in itself but a symptom of an underlying medical condition. The term “sciatica” describes the pain that originates in the lower back and travels down the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the body, running from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg.
Common Causes of Sciatica
Several conditions can cause sciatica, including:
Slipped or Herniated Disc:
- One of the most common causes of sciatica. It occurs when the soft inner gel of the disc pushes through the outer layer and presses on the sciatic nerve.
Spinal Stenosis:
- This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress the nerves, including the sciatic nerve.
Piriformis Syndrome:
- A neuromuscular disorder that occurs when the piriformis muscle compresses the sciatic nerve. This muscle is located in the buttocks near the top of the hip joint.
Pelvic Injury or Fracture:
- Trauma to the pelvic area can affect the sciatic nerve, causing pain and other symptoms.
Tumors:
- Though rare, tumors can form on the spinal cord or the sciatic nerve, leading to sciatica.
Spondylolisthesis:
- A condition where
- one vertebra slips over another, potentially compressing the nerve roots that form the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms of Sciatica
The primary symptom of sciatica is pain that radiates from the lower back to the buttock and down the back of the leg. This pain can vary in intensity from a mild ache to a sharp, burning sensation or excruciating discomfort. Other symptoms may include:
- Numbness: In the affected leg or foot.
- Tingling: Or a pins-and-needles feeling in the toes or part of the foot.
- Weakness: In the leg or foot.
- Difficulty Moving: Or controlling the leg due to muscle weakness.
Sciatica symptoms often worsen with prolonged sitting, standing, or walking.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing sciatica, including:
- Age: Age-related changes in the spine, such as herniated discs and bone spurs, are the most common causes of sciatica.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can increase stress on the spine.
- Occupation: Jobs that require heavy lifting, twisting the spine, or driving for long periods can contribute to the risk of sciatica.
- Prolonged Sitting: People who sit for long periods or lead a sedentary lifestyle are more likely to develop sciatica.
- Diabetes: This condition increases the risk of nerve damage, including sciatica.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing sciatica involves a physical examination and reviewing medical history. In some cases, imaging tests may be necessary to determine the exact cause of sciatica. These tests can include:
- X-rays: To look for bone spurs or other conditions affecting the spine.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): To create detailed images of the spinal cord and nerves.
- CT Scans: Sometimes used with a dye to get a clearer picture of the spinal cord and nerves.
- Electromyography (EMG): To measure the electrical activity of muscles and nerves.
Treatment Options
The treatment for sciatica depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Some common treatments include:
Medications:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Prescription medications for more severe pain.
- Muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Physical Therapy:
- Exercises to improve posture, strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, and improve flexibility.
Steroid Injections:
- Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and pain around the affected nerve roots.
Surgery:
- Reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed, or there is significant nerve compression leading to muscle weakness or loss of bowel or bladder control.
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy can provide relief for some individuals.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of sciatica can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening the muscles of the back and abdomen to support the spine.
- Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting objects.
- Ergonomic Work Environment: Ensuring that your workspace supports good posture and minimizes strain on your back.
- Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the spine.
Seeking Professional Help
If you experience symptoms of sciatica, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice. The Spine Clinic, with locations in Bandra, Churchgate, Goregaon, Borivali, Raipur, and Bhopal, offers specialized care for spine-related issues, including sciatica. The clinic provides comprehensive diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to help manage and alleviate sciatica symptoms effectively.
Contact Information
For appointments and consultations, you can reach out to the Spine Clinic at:
- Phone: 8657500555 / 9619010123
- Website: Mumbai Spine Clinic
Conclusion
Sciatica can be a debilitating condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage and alleviate pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing long-term damage and improving quality of life. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of sciatica, don’t hesitate to seek expert care from a specialized clinic like the Spine Clinic in Mumbai. Their team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing the best possible care to help you live a pain-free and active life.